Ichneumonidae glossary
For more detail see the online list of hymenoptera anatomy terms.A B C E F G I M N O P S T
A | ||
|---|---|---|
| Antennae | sensory organs consisting of the scape, pedicel and flagellum |
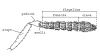
Labelled antenna (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
| Apterous | without wings |
|
| Areolet | a small inclosed area on the forewing |
Labelled forewing (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
B | ||
| Brachypterous | partly winged |
|
C | ||
| Carinae | ridges |
|
| Cosmopolitan | occurring throughout, generally in reference to world-wide occurrence |
|
E | ||
| Ectoparasite | species whose larvae develop externally on the host |
|
| Endoparasite | species whose larvae develop internally in the host |
|
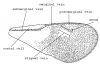
| Epicnemial carina | a carina (ridge) that is sometimes present anteriorly on the mesopleuron |
Labelled lateral view of body (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984). |
F | ||
| Face | part of the head below the antennal sockets and includes the clypeus |
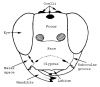
Labelled head (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
| Flagellum | segments of the antennae excluding the pedicel and scape. Segments are numbered from the most proximal (which is 1) |

Labelled antenna (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
| Frons | part of the head above the antennal sockets of an insect's head, usually has an ocellus |
Labelled lateral view of body (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984). |
G | ||
| Glymma | pit-like structure on T1 |
|
I | ||
| Instar | a stage of a developing larva |
|
M | ||
| Macropterous | fully winged |
|
| Malar space | space between bottom of the eye and mandible, sometimes with a groove |

Labelled head (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
| Mesopleuron | laterally, the middle segment of the mesosoma; containing the middle leg |
Labelled lateral view of body (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984). |
| Mesoscutum | dorsally, the middle segment of the mesosoma |
Labelled lateral view of body (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984). |
| Mesosoma | the combined thorax and propodeum. In most Hymenoptera the first abdominal segment (propodeum) is fused to the reduced metathorax |
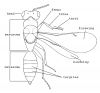
Labelled dorsal habitus (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
| Metasoma | the abdomen less the propodeum (corresponds to the gaster of some authors) |

Labelled dorsal habitus (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
N | ||
| Notauli | a pair of grooves arising from the front margin of the mesoscutum and extending posteriorly |
|
O | ||
| Ocellus | small simple eye (pl = Ocelli) found on top of head |

Labelled head (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
| Ovipositor | in females, egg-laying device, protected by a pair of ovipositor sheaths |
|
P | ||
| Pectinate | toothlike projections (like those on a comb) |
|
| Pedicel | the second segment of the antennae |

Labelled antenna (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
| Propodeum | the first abdominal segment in Hymenoptera. It is fused with the thorax to form the mesosoma. It is often subdivided by carinae into a number of areae |
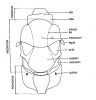
Labelled dorsal mesosoma (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
S | ||
| Scape | basal segment of the antennae |

Labelled antenna (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
| Sclerotised | hardened |
|
| Spiracle | small openings on the surface (associated with respiration) |
|
| Sternalus | broad shallow groove extending from the epicnemial carina towards the lower hind corner of the mesopleuron |
|
| Sternite | a sternite is a hardened plate on the ventral surface, for example on the metasoma. Numbered S1, S2, S3 etc |

Labelled dorsal habitus (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
T | ||
| T1 | Tergite number 1 |
|
| Tergite | tergites are hardened plates on the dorsal surface, for example on the metasoma. Numbered T1, T2, T3 etc |

Labelled dorsal habitus (figures modified with permission from Noyes & Valentine 1989; and Gauld 1984) |
