Greenroofs

Greenroofs are vegetated roof covers, with growing media and plants taking the place of bare membrane, shingles, tiles or other roofing materials.
The primary reason for greenroofs in cities is for stormwater retention (delay in runoff) and reduction of stormwater volume entering piped drainage infrastructure.
In many cities around the world greenroofs are also used to:
- improve runoff quality (especially where acid rain, high dust/traffic volumes or Cu/Zn (copper/zinc) roof features)
- modify city temperatures and reflectance leading to increased energy efficiency of building
- create or enhance biodiversity: habitat for plants, insects, and birds.
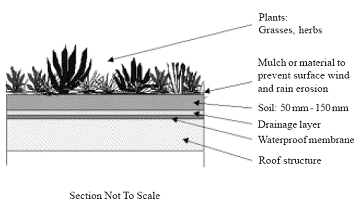 The number of layers and the layer placement vary from system to system and greenroof type. However, all greenroofs at least include a single to multi-ply waterproofing layer, drainage, growing media and the plants. Grasses, trees and shrubs may be used, though various species of sedum are most commonly used in many greenroof applications (note: sedums are weeds in some New Zealand environments). In New Zealand both exotic and native species can be used.
The number of layers and the layer placement vary from system to system and greenroof type. However, all greenroofs at least include a single to multi-ply waterproofing layer, drainage, growing media and the plants. Grasses, trees and shrubs may be used, though various species of sedum are most commonly used in many greenroof applications (note: sedums are weeds in some New Zealand environments). In New Zealand both exotic and native species can be used.
Commonly, the roof function or objective of the roof space determines the design – is it just an ecological cover or is it intended for human recreation, vegetable gardening, etc.? The limiting factors for greenroofs include: the roof loading capacity or maximum dead and live weight loads, determined by a structural engineer; the slope of the roof, and perhaps the client’s budget.
