ICHNEUMONIDAE: : Glabridorsum Townes 1970
Diagnosis:
Glabridorsum has very distinct black and white stripes on the metasoma.Characteristics of Glabridorsum include: 1. Body size <10mm; 2. Position of spiracle on T1 of metasoma clearly behind the centre; 3. Shape of aerolet in forewing pentagonal (closed) or triangulate; 4. Colour of face not all black; 5. Metasoma compressed dorsal-ventrally; 6. Size of ocelli small; 7. Length of antennae as long, or longer than body; 8. Length of ovipositor not longer than body; 9. Wings present; 10. Colour of wings hyaline (clear); 11. Sternaulus short to long; 12. Shape of face in lateral view flat or only weakly bulging; 13. Sternite on T1 (viewed laterally) not extending past spiracle; 14. Shape of T1 (viewed laterally) evenly curved; 15. Number of teeth in mandibles 2; 16. Metasoma with distinct black and white stripes; 17. Length of T1 less than T2 or subequal in length; 18. Sculpture on mesoscutum finely pitted, many hairs; 19. Width of T1 (viewed dorsally) anterior part slender often parallel, strongly widening behind spiracle; 20. Glymma on T1 absent; 21. Sculpture on metasoma smooth with a semi-glossy or satin appearance at least on T2; 22. Propodeum reaching past coxal insertion, but not reaching halfway along metacoxae.
Similarity to Other Taxa
Based on the distinct black and white stripes on the metasoma, Glabridorsum can only be confused with Xanthocryptus . In Xanthocryptus the spiracle on T1 is at, close to, or before centre; areolet in the forewing is small, and the white bands around the eyes are broken (they are continuous in Glabridorsum ). See Green (1984. A diagnostic aid. The Weta 7 : 65-67) for further help.Distribution in NZ
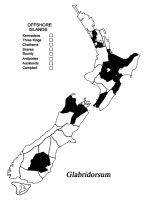
North Island: AK, BP, HB, TO, WN. South Island: NN, MB, CO.
Species in NZ
One introduced biological control agent, Glabridorsum stokesii (Cameron 1912).Biology & hosts
Many species in this genus occur in the Indo-Australian region (Gauld 1984). One Australian species, G. stokesii , is a well-known parasitoid of economically important fruit pests (Russell 1987).Glabridorsum stokesii was introduced into New Zealand in 1967-1969 for biological control of the oriental fruit moth Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) and the light brown apple moth, Epiphyas postvittana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) (Cameron et al 1989). Although its impact on these pests is variable, it is relatively common.It has also been recorded from two non-target native species Ctenopseustis obliquana , and Planotortrix excessana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Overseas it is has also been recorded from Xylorycta luteotactella (Oecophoridae) and the codling moth, Cydia pomonella (Tortricidae) (Yu et al. 2005).
Sources of information
Cameron PJ, Hill RL, Bain J & Thomas WP. 1989. A Review of Biological Control of Invertebrate Pests and Weeds in New Zealand 1874-1987. Technical Communication No 10. CAB International Institute of Biological Control. DSIR Entomology Division. 424 p.Gauld ID 1984. An Introduction to the Ichneumonidae of Australia. London, British Museum (Natural History). 413 p.
Green OR. 1984. A diagnostic aid. The Weta 7 : 65-67.
Russell DA. 1987. Glabrodorsum stokesii (Cameron) (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) – a parasitoid of the oriental fruit moth ( Grapholita molesta ) in New Zealand. New Zealand Entomologist 10: 26-38.
Yu DS, van Achterburg K, Horstmann K. 2005. World Ichneumonoidea 2004. Taxonomy, Biology, Morphology and Distribution. CD/DVD. Taxapad. Vancouver, Canada.
Citation
Ward DF & Schnitzler FR. 2013. Ichneumonidae of New Zealand. Genus Glabridorsum http://ichneumonidae.landcareresearch.co.nzAccessed: 27 April 2025