Working with Zespri
This page focuses on footprinting work with Zespri in recent years, explaining how, working with other Crown Research Institutes, GHG footprinting has been used to enhance the reputation and premium quality offering of New Zealand horticulture.

GHG Footprints
Greenhouse gas (GHG) footprinting, also more commonly referred to as a carbon footprint, determines the total volume of GHG emitted, in carbon equivalents (CO2e), across the entire supply chain (life cycle) of a product or service. GHGs include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons CFCs, propane, butane, etc. GHG footprinting can be used to determine the volume of CO2-e. by one kilo of kiwifruit grown and packaged in New Zealand, transported to the United Kingdom, sold and consumed, in the month of July.
Work led by Landcare Research, supported by Plant and Food Research, AgriLINK New Zealand, and Massey University, produced an indicative sector carbon footprint for ZESPRI® GREEN, GOLD and ORGANIC Kiwifruit for Zespri International Ltd and the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry.
The kiwifruit study modelled the carbon footprint of green, gold and green organic kiwifruit based on data from 61 orchards and 10 coolstores/packhouses (based on the 2002/3 and 2003/4 seasons).
The GHG footprint included all operations from growing and picking fruit in orchards, through the storage and shipping, to being eaten and disposed of by consumers. The ISO 14040 and 14044 standards on Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) were followed for the analysis, and their interpretation in the British Standards Institute PAS 2050 specification was also taken into account.
LCA assesses a wider range of activities than those required when using the PAS 2050 approach. In particular, it differs through the inclusion of production and maintenance of orchard capital (such as tractors) and the inclusion of consumer transport.
The wider assessment ensures that the industry can respond to future changes in the PAS 2050 as well as the final outcomes of international standards currently under development for carbon footprinting and communication (for example, in the International Standards Organisation). The study was peer reviewed by staff at the Swedish Institute for Food and Biotechnology (SIK).
Results
Carbon emissions for the key stages of a ZESPRI® kiwifruit's lifecycle are (based on all exports of New Zealand Kiwifruit to the world (see Figure 1):
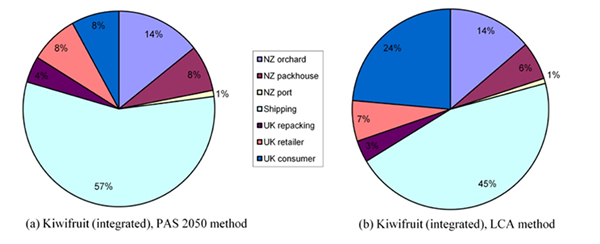 |
| Figure 1: Carbon emissions for the key stages of a ZESPRI® kiwifruit's lifecycle are (based on all exports of New Zealand Kiwifruit to the world) |
The comprehensive understanding of GHG emissions enables Zespri to develop effective plans to reduce GHG emissions throughout the supply chain, significantly improving the footprint.
Further actions
- ZESPRI carbon footprint methodology has now been adopted as the international product rule for the lifecycle measurement in kiwifruit.
- Development of information technology systems is underway to record and monitor changes in the carbon/greenhouse gas footprint of our products.
- Ongoing research to identify and prioritise initiatives to reduce emissions across the product lifecycle.
