Antarctic Features

Possession Island, Ross Sea. Image - Phil Lyver
The Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean comprises about 10% of the world's oceans. It completely surrounds Antarctica and contains the coldest and densest water on earth. The Southern Ocean also has the highest biological productivity of any ocean. This is due largely to the rapid growth of phytoplankton fed by rich supplies of nutrients welling-up in the region of the Antarctic Convergence.
The Antarctic Convergence
This is a boundary between cold, north-flowing surface water (a floating layer of less dense water from melting sea-ice and icebergs which is less salty than normal seawater), and relatively warm sub-Antarctic water.
Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC)
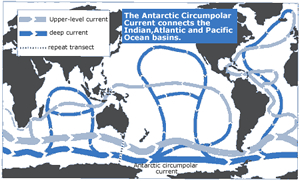
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), sometimes called the "great ocean conveyor", connects the three great ocean basins, Atlantic, Indian and Pacific, allowing water, heat, salt and other properties to flow from one to the other. Some of the seawater in the ACC travels the 24 000 km around the world in about 8 years. The ACC also plays an important role in controlling our climate. The ACC connects the world's oceans and redistributes heat influencing temperature and rainfall world wide.
 |
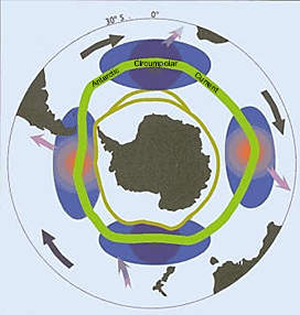 |
| The ACCconnects the Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific Ocean basins. | Path of the ACC around Antarctica. |
The Antarctic Circle
This is a circle around the earth at 66°3'S. Anyone at this spot on 22 December, the summer solstice, will notice that the sun does not set — there will be a 24 hr day! Conversely, on 21 June, the winter solstice, the sun will not rise and there will be 24 hrs of darkness.
The South Pole
First reached by Amundsen in 1911, the South Pole is as far south as one can go. At the bottom of the globe, hundreds of kilometres from the ocean and with clear skies free of water vapour, the South Pole is a near perfect window to the Universe (nearly as good as the Hubble telescope). Astrophysicists use instruments such as radio-, infrared-, and microwave telescopes to measure background radiation like muons and neutrinos, allowing us to look back 13 billion years to the birth of the universe.
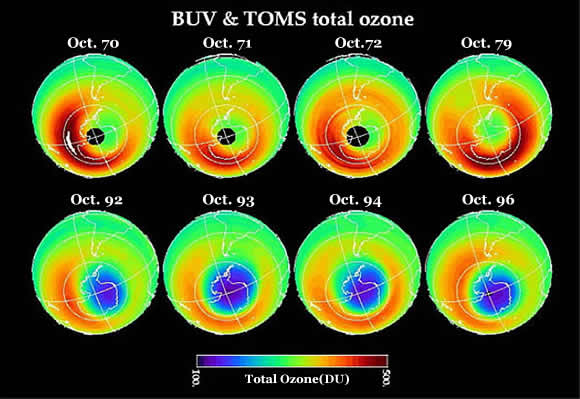
The Ozone Hole
Stratospheric winds high in the earth's atmosphere carry pollutants such as CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons), southwards over Antarctica, where they mix with high altitude clouds in winter. In summer the sun's rays release chlorine molecules from the clouds that then react with and destroy the thin ozone layer. The ozone layer is important in screening the damaging effects of solar radiation from living things.
 |
