Basic cliffs, scarps and tors

Outcrop on Mt Herbert, Banks Peninsula, Canterbury, with vegetation comprising stunted shrubs, grasses and herbs (Susan Wiser)
These cliffs, scarps, and tors occur inland on tuffaceous sandstones and mudstones, andesite, diorite, basalt, and gabbro. Plant species are tolerant either of shallow soils, full sunlight, and intermittent drought, or damp and shady crevices. They are either restricted to the low-competition environment of these habitats, or derived from the surrounding matrix and able to survive in the harsh conditions.
Synonyms
Mafic cliffs, scarps and tors.
Where do they occur?
Basic cliffs, scarps, and tors occur throughout the North Island and are especially prominent in Northland and the Coromandel Peninsula. In the South Island they occur on Banks Peninsula, the Otago Peninsula, and at scattered locations in western Southland, eastern Otago, south Canterbury, central Marlborough and NW Nelson.
-
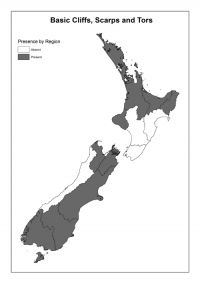
Basic cliffs, scarps and tors:
Presence by Region -
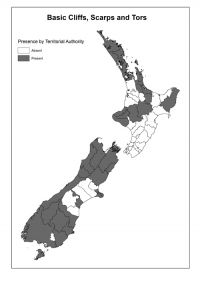
Basic cliffs, scarps and tors:
Presence by Territorial Authority
Notable flora and fauna
Threatened and rare plants include nationally critical Lyttelton forget-me-not (Myosotis lytteltonensis), Puketi haresfoot fern (Davallia tasmanii subsp. cristata), Adam’s koromiko (Veronica adamsii), Maungarahu rock hebe (Veronica saxicola), pygmy button daisy (Leptinella nana), nationally endangered Bartlett’s koromiko (Veronica perbella), Coprosma waima and Olearia crebra, nationally vulnerable rock koromiko (Veronica bishopiana), Jersey fern (Anogramma leptophylla), the declining Veronica lavaudiana and the naturally uncommon blanket fern (Asplenium subglandulosum), Senecio glaucophyllus subsp. basinudus, Kowhai (Sophora fulvida), and the Banks Peninsula aniseed (Gingidia enysii var. peninsulare).
Threatened and rare fauna include the Canterbury gecko (Hoplodactylus aff. maculatus ‘Canterbury’), the spotted skink (Oligosoma lineoocellatum), the Banks Peninsula tree weta (Hemideina ricta; although it is likely that they only occupy refuges amongst rocks in situations where they face a shortage of refuges in trees or logs) and two narrowly distributed lichen-feeding beetles (Artystona wakefieldii and A. rugiceps).
Threat status
Vulnerable (Holdaway et al. 2012)
Threats
Weed invasion, especially by woody weeds, can be a serious problem as these species can out-compete existing native species and readily colonise available habitat as it arises, pre-empting establishment by native species. Some especially problematic woody weeds are gorse (Ulex europaeus), Scotch broom (Cytisus scoparius) and pines (Pinus spp.). Herbaceous weeds include pampas grass (Cortaderia selloana), common polypody (Polypodium vulgare), spur valerian (Centranthus ruber), pigs ear (Cotyledon orbiculata), fennel (Foeniculum vulgare), Mexican daisy (Erigeron karvinskianus) and wallflower (Cheiranthus cheiri). Invasive weeds are most serious where the cliffs, scarps and tors are near urban areas or embedded in an exotic matrix, especially in frost-free environments. Spray drift during weed control operations can destroy desirable native plants nearby. Browsing by goats or possums may be a serious threat. In dry, eastern areas, destruction of vegetation by fire can be an issue. Vegetation may also be damaged from recreational (mainly rockclimbing) overuse.
Further reading
De Lange PJ 1998. Hebe perbella (Scrophulariaceae) - a new and threatened species from western Northland, North Island, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Botany 36: 399-406.
von Konrat MJ, Braggins JE, de Lange PJ 1999. Davallia (Pteridophyta) in New Zealand, including description of a new subspecies of D. tasmanii. New Zealand Journal of Botany 37: 579-593.
Wiser SK 2001. Montane rock outcrops: islands of biodiversity on Banks Peninsula. Canterbury Botanical Society Journal 35: 32-36.
Wiser SK, Buxton RP 2008. Context matters: matrix vegetation influences native and exotic species composition on habitat islands. Ecology 89: 380-391.
Wiser SK, Buxton RP 2009. Montane outcrop vegetation of Banks Peninsula, South Island, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Ecology 33: 164-176.
Links
The war on pests: Dealing to key pest plants and animals that threaten native species (see MODULE 2: Rocky outcrops – hotspots of native biological diversity). Banks Peninsula Conservation Trust and Environment Canterbury
